Brazil Installs First In-Ovo Sexing Machine: Major Milestone for Latin American Egg Industry and In-Ovo Sexing
Source: AAT and Hy-Line do Brazil
Agri Advanced Technologies (AAT) has partnered with Brazilian egg producer Raiar Orgânicos to implement the first ever in-ovo sexing machine in Latin America. AAT’s “Cheggy” in-ovo sexing system has been installed and is now operating successfully in a Hy-Line do Brasil hatchery.
"With our launch in Brazil, we’re expanding the range of available solutions for sustainable and humane egg production," says Jörg Hurlin, Managing Director of AAT. "In-ovo sexing allows for early selection in the hatchery and offers a scalable, efficient approach – making it particularly suitable for large markets like South America."
Though Brazil’s Committee on Environment and Sustainable Development of the Chamber of Deputies moved forward legislation on the common practice of male culling in late 2024, this market-driven announcement by Raiar Orgânicos and AAT was driven by strict business calculus. The egg producer pursues a holistic approach to win customers that combines animal welfare, support for regional agriculture, and technological innovation. By converting their entire flock to use in-ovo sexing, the company is pioneering a bold and more ethical new standard for Brazilian egg production.
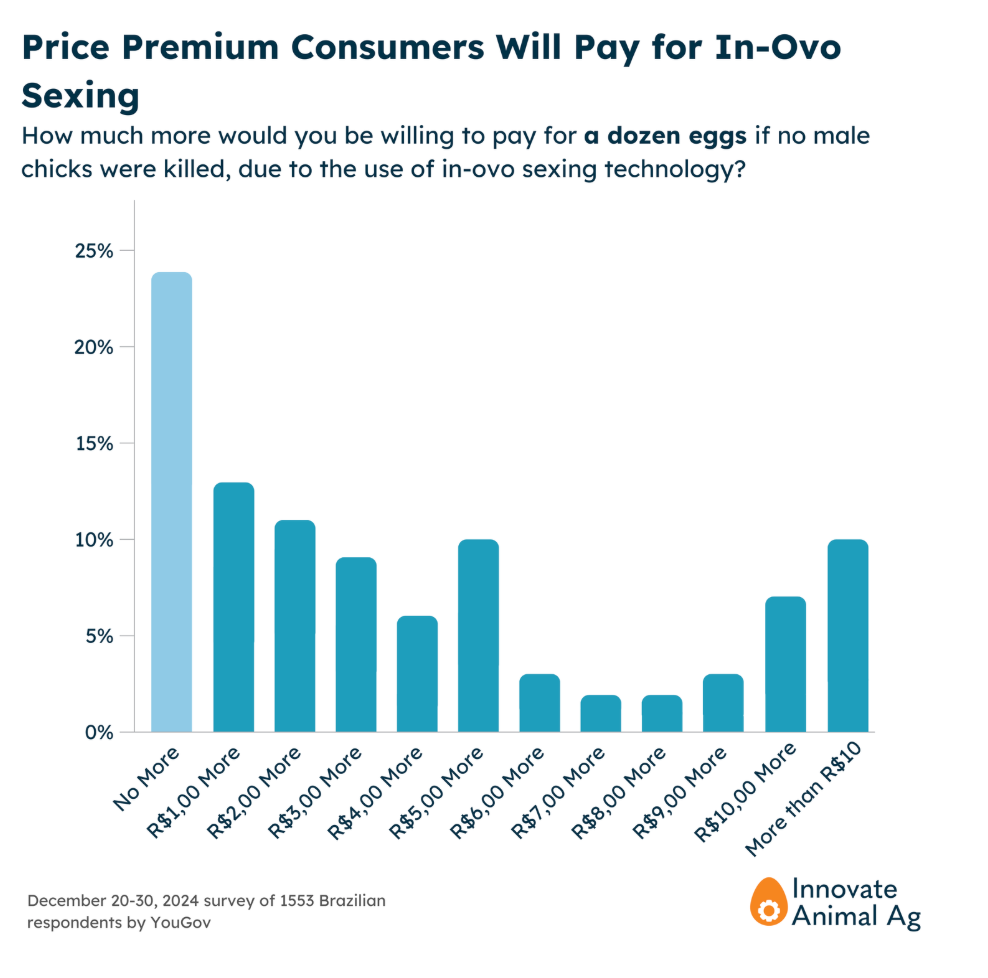
This demonstration of industry leadership is supported by recent consumer polling. Innovate Animal Ag’s Brazilian consumer survey highlighted a strong potential market demand for a new product and branding using in-ovo sexing technology. 76% of Brazilian egg buyers were willing to pay a premium for eggs made with the technology. On average, the survey revealed an average willingness to pay R$5.00 (or $0.88 USD) extra per dozen.
“Raiar Orgânicos is setting an inspiring example of what forward-thinking leadership looks like in animal agriculture,” said Robert Yaman, CEO of Innovate Animal Ag. “As in-ovo sexing becomes a global trend, we’re excited to see companies like Raiar not only embrace the change but help drive it. With technologies like Cheggy now available in Brazil, this milestone should serve as a powerful catalyst for more producers across the country.”
Several other major egg producers in Brazil had already announced plans to adopt in-ovo sexing technology once it became commercially available, and with the installation of the Cheggy machine they’ll now have this opportunity.
This development also arrives at a critical moment for in-ovo sexing. The technology has recently hit a notable 28% market penetration in the European Union and is now rapidly expanding in countries without bans like Norway, Switzerland, the Netherlands, and the United States. In the US, the egg producer NestFresh recently debuted their Humanely Hatched™ eggs to bring in-ovo sexing to US consumers.
It takes around 18 to 24 weeks for chicks to start producing eggs, meaning the first Brazilian eggs produced using in-ovo sexing should start hitting the shelves for Raiar Orgânicos in early 2026.
For more information about in-ovo sexing technology and market trends, read our2025 In-Ovo Sexing Market Penetration and Forecast Report or explore ourBrazilian Consumer Survey findings.